Recently, the team led by Associate Researcher Liu Chengbo from the Center for Biomedical Optics and Molecular Imaging, Institute of Medical and Biological Engineering, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, the team led by Researcher Zhang Peng from the Translational Medicine Center, and the team led by Professor Ding Dan from Nankai University have successfully achieved research on photoacoustic molecular imaging for the diagnosis and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Based on the three-dimensional photoacoustic molecular imaging technology in the second near-infrared region (NIR-II), combined with a highly specific tocilizumab-conjugated polymer nano-diagnostic and therapeutic agent for rheumatoid arthritis, this study successfully achieved the early assessment and diagnosis of the degree of inflammation in a mouse model of rheumatoid arthritis and accurately monitored the therapeutic effect of rheumatoid arthritis. The related research work "Tocilizumab-Conjugated Polymer Nanoparticles for NIR-II Photoacoustic Imaging-Guided Therapy of Rheumatoid Arthritis" was published in *Advanced Materials* (Jingqin Chen et al., Advanced Materials, 2020, 2003399, with an impact factor of 27.398). Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a common immune osteoarticular inflammatory disease with insidious onset and unknown etiology. In the early stage, symptoms such as redness, swelling, heat, and pain occur. As the disease progresses, bone erosion occurs in the osteoarticular joints, ultimately leading to disability. Early diagnosis and treatment of RA are crucial for the prognosis. Compared with tumor lesions, RA lesions have a higher blood background, and inflammatory factors are distributed in the cartilage and joint capsules, posing a greater challenge to photoacoustic molecular imaging. Photoacoustic molecular imaging in the NIR-II region enables highly sensitive and specific imaging with a large penetration depth, providing a new strategy for imaging-guided diagnosis and treatment of RA. The research team independently developed cutting-edge international photoacoustic molecular imaging technology. Based on the conjugated polymer nano-preparation (TCZ-PNPs) modified with the RA-targeted therapeutic antibody tocilizumab (TCZ), they achieved challenging high-quality imaging at the in vivo level. The research results show that TCZ-PNPs have excellent optical properties and biocompatibility, as well as good targeting ability to RA joint lesions. Under the guidance of three-dimensional photoacoustic molecular imaging, it is possible to accurately and non-invasively diagnose RA joint tissues in the early stage, with an image signal-to-noise ratio as high as 35.8 dB. After a one-month treatment using TCZ-PNPs, the PA monitoring results show that the symptoms of RA joints can be effectively suppressed. The results of photoacoustic diagnosis and treatment are consistent with those of Micro-CT imaging and histological analysis. This work well demonstrates that the photoacoustic molecular imaging technology in the NIR-II region can achieve highly sensitive and specific imaging of RA lesions, providing a new strategy for the diagnosis and treatment of RA and the monitoring of RA treatment. This research is supported by major research programs of the National Natural Science Foundation of China, key research and development programs of the Ministry of Science and Technology, and instrument development projects of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
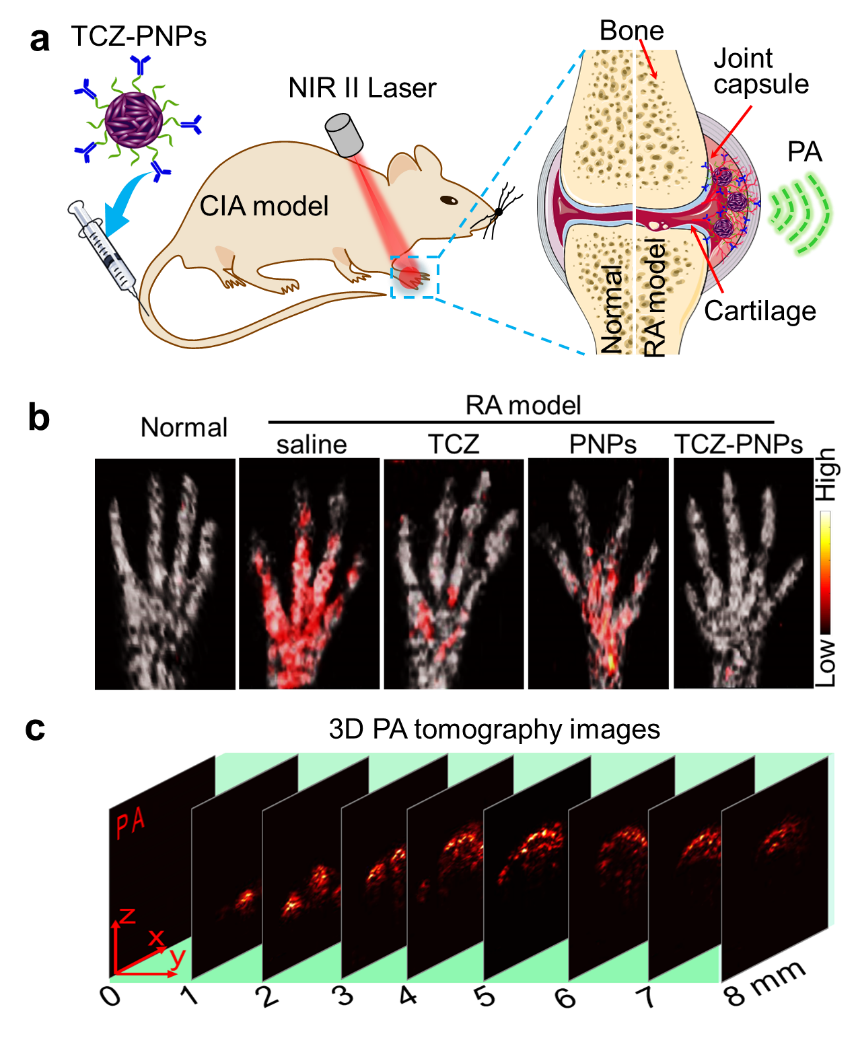
(a). Schematic diagram of the imaging and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in mice; (b). Photoacoustic diagnostic images of the paws of mice with rheumatoid arthritis; (c). Three-dimensional tomographic images of the paws of mice with rheumatoid arthritis.