Recently, the research team of Researcher Liu Chengbo from the Center for Biomedical Optics and Molecular Imaging, Institute of Biomedical and Health Engineering, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, the research team of Researcher Liang Dong from the Center for Medical Artificial Intelligence, and the research team of Professor Zheng Chuansheng from the Department of Radiology, Wuhan Union Hospital, have collaborated to propose a low-dose photoacoustic imaging method based on a convolutional neural network. This method is expected to further promote the clinical transformation of photoacoustic imaging technology. The related work "Deep learning enables superior photoacoustic imaging at ultra-low laser dosages" was published in Advanced Science (DOI: 10.1002/advs.202003097, IF: 15.84). In this study, the first authors are Dr. Zhao Huangxuan from Wuhan Union Hospital (a visiting student at Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology) and Doctoral Student Ke Ziwen from Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology. Researcher Liu Chengbo and Researcher Liang Dong from Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, and Professor Zheng Chuansheng from Wuhan Union Hospital are the co-corresponding authors. Photoacoustic imaging can non-invasively obtain high-resolution morphological and functional information of organisms and the human body, and it is a new generation of medical imaging technology that has the potential for significant breakthroughs. Limited by laser safety, the laser energy that biological tissues can withstand is limited. Especially in high-speed imaging, the safety of laser energy is currently a bottleneck problem restricting the development of this technology. Laser dosage, imaging speed, and image quality are mutually restrictive in photoacoustic imaging, hindering the wider application of the technology in clinical and basic research. Up to now, there is still a lack of good solutions. The research team of this study proposed a convolutional neural network method of a multi-task residual dense network (MT-RDN), which effectively solves this problem. By using a multi-supervised learning strategy to mine the complementary information in the photoacoustic spectral domain, and based on a dual-channel network and adaptive weight distribution, the team achieved high-quality imaging under low-dose laser irradiation and obtained ultra-low-dose photoacoustic images that are 32 times lower than the laser safety threshold. To meet the need of simultaneously obtaining multi-wavelength and multi-dose data required by the neural network, the team carried out innovations in photoacoustic imaging technology and achieved continuous imaging with four laser pulses. This work is expected to further promote the clinical application of photoacoustic imaging technology, especially in scenarios of low laser dosage and high-speed imaging. This research project is supported by the Major Research Plan of the National Natural Science Foundation of China, General Programs of the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Instrumentation Team of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Youth Instrumentation Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the Youth Innovation Promotion Association of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, etc.
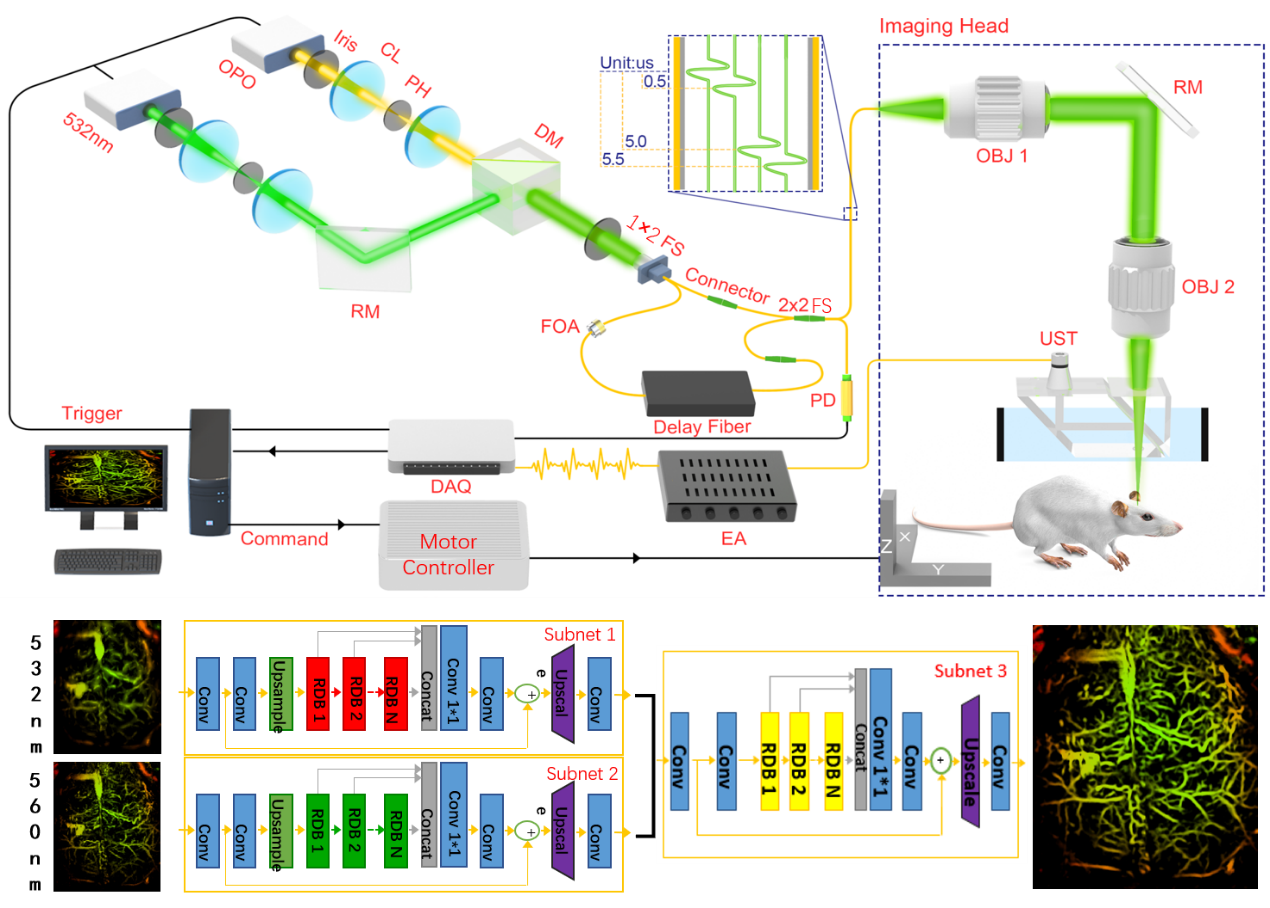
Figure 1. At the top is a schematic diagram of the photoacoustic imaging system. At the bottom, from left to right, are the dual-wavelength input image, the framework of the multi-task residual dense network, and the output image of the convolutional neural network